- Short History of the Internet in Nepal
- Beginning of the Internet In Nepal
- Launch of Real Internet Connection in Nepal
- Introduction of Wireless Internet With Better Speed
- Introduction of Cable Internet in Nepal
- GPRS And 3G Internet In Nepal
- Nepal Telecom ADSL Connection and WiMax
- The Golden Era of Fibre Optics-based Internet in Nepal
- The Evolution Of 4G, LTE, VoLTE Internet in Nepal
- 5G – The Dirty Politics
- Access to the Internet in Nepal in Rural Areas
- Growth of Users of the Internet in Nepal
- Current Statistics of Access To The Internet in Nepal
Short History of the Internet in Nepal
In this interconnected world, the Internet is a vital tool for global communication. It has evolved into a priceless resource that condenses the entire world onto a small screen. Join me as we delve into the history and advancements of Internet speed in Nepal.
Beginning of the Internet In Nepal
The Internet was initially launched as a mechanism of communication in the military by the US Department of Defense in 1983. And it was so revolutionizing that it was decided to be used for general communication. So, the internet was launched in the world globally in 1990 AD.
The internet was introduced in Nepal in 1994 which is just after 4 years of the initial global launch. We can not say, it took a lot of time because it was the first time that new technology was being introduced which requires a heavy investment of physical infrastructure.
The introduction of new technology within a short period was a proud moment, but when it comes to accessibility internet in Nepal in its initial days was too limited to very few people and organizations.
Mercantile, which is popularly known for providing free .np domain for Nepalese, hosting service, and banking software in Nepal was the first company to launch the internet in Nepal.
Mercantile Communication introduced the Internet in Nepal in collaboration with the ROYAL NEPAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, an autonomous government body that is currently known as the Nepal Academy of Science and Technology.
This system being limited in capacity was only able to serve email systems based on dial-up technology whose bandwidth was being imported from Australia. It was costly and limited to very few people and organizations.
Launch of Real Internet Connection in Nepal
The experience of the Internet in Nepal could be felt only after 1995 AD. This became possible only after the introduction of the Internet in Nepal by WorldLink Communication, established as a private company.
Currently, WorldLink is the largest internet service provider in Nepal which was established in 1995 AD. It started providing internet in Nepal through a dial-up connection modem.
The dial-up connection modem used to produce irritating noise and the maximum speed a user could get under a favorable situation was 56 Kbps. The cost for the internet was on a per-minute basis. It means that users were not guaranteed to get a proper connection but still had to pay per minute basis which makes it costly.
From better management and use of technology, WorldLink was able to provide better internet service at a lower cost than Mercantile Communication and it was also providing email service at the same time. To heat the competition, Mercantile started providing free .np domains for Nepalese.
The downside of dial-up connection was that it was dependent on the telephone line which means that the user could either make a phone call or use the internet at a time. Using both at the same time was impossible. The speed was up to 56 Kbps and would cost per minute basis regardless of the speed.
Introduction of Wireless Internet With Better Speed
Since telephone line-based dial-up had so many issues and downsides, to solve this problem a new technology was introduced in the market that would work wirelessly. WorldLink adopted this technology and in 2003 AD, it introduced wireless internet in Nepal which managed to provide a massive jump in the speed from 56Kbps to 256Kbps.
This solved the problem of noise that dial-up connections used to make, slower speed, and the problem of not being able to use the telephone and internet simultaneously. This quickly made the internet more popular in Nepal within a short span of time.
Introduction of Cable Internet in Nepal
Cable internet was started in Nepal in 2005 AD by Subisu Cablenet Ltd., a private company. It was established in 2001 AD and started its’ venture through a Cable TV Service provider.
Subisu was the first company to launch broadband internet in Nepal using DOCSIS Technology based on Hybrid Fiber Coaxial Cable to provide dual play service of Internet and TV over the same cable.
The cable connection provided by Subisu was completely different than the cable of the dial-up connection which was a telephone line. Subisu cable was a separate cable that was being used for TV connection and internet connection.
This advancement in technology made the internet more affordable, fast, and popular among users as they could get both TV and internet service without having to pay for these cables separately.
However, all these services and service providers were concentrated around the urban areas, especially Kathmandu city. So access to the internet in Nepal was not available in rural areas.
GPRS And 3G Internet In Nepal
GPRS technology was introduced in Nepal in 2005 AD by Mero Mobile (now Ncell), a private telecommunication company. This increased access to an internet connection. Mig33 and Nimbuzz were used excessively as social media during this period.
3G technology was introduced in the World in the early 2000s and was already being used when Nepal was struggling with dial-up connections. The 3G connection was introduced in Nepal on May 17, 2007. Interestingly, 3G was introduced in Nepal before India. India launched 3G on 11 December 2008, and adapted commercially only after 2009.
Initially, the 3G connection was so expensive that it would cost around Nrs 4000.00 to 5000.00 just to get a 3G compatible SIM card that is too long with a very long queue of waiting.
The launch of 3G was a milestone that enabled video streaming online in HD quality, made it possible to make video calls, and unlocked the possibility of the internet in many aspects. The average stable speed one could get with 3G internet was around 2-10 Mbps. Later it was upgraded to 3.5G aka HSDPA/ HSPA which took the speed up to 14 Mbps making mobile internet in Nepal more appealing for mobile users.
Unfortunately, these upgrades were done in profitable and city areas only and the rural areas were using the GPRS-based 2G connection or even older 1G network.
Nepal Telecom ADSL Connection and WiMax
Just one year after the launch of 3G, Nepal Telecom introduced its broadband connection ADSL. Asymmetric digital subscriber line (ADSL) is a type of digital subscriber line technology, that enables faster data transmission over copper telephone lines than a conventional voiceband modem.
ADSL was not as good as 3G mobile internet in terms of speed as it was offering just 512Kbps of maximum upload and download speed.
The combination of 3G in the mobile network and the introduction of ADSL revolutionized the internet market of Nepal. It created a sudden leap in the number of people using the internet connection. The statistics show that the population having access to the internet rose to 9% in 2011 AD which was just 1% before the launch of 3G and ADSL in 2006 AD.
Similarly, in 2013 Nepal Telecom also introduced WiMax, a home broadband solution that was able to provide speeds up to 512Kbps. This was not a worthy project as there was high maintenance cost and lower speed. Nepal Telecom has already upgraded the ADSL and WiMax users to its Fibre technology-based connection and retired the copper wire connection.
The Golden Era of Fibre Optics-based Internet in Nepal
This revolutionary technology was introduced in Nepal by ViaNet in 2011 AD. While Nepal Telecom was planning to launch copper wire-based WiMax, Vianet already started the best technology to provide a super fast broadband connection. Fibre optics is the best technology for data transmission commercially available to date based on the total internal reflection of light rays.

After the introduction of Fibre optics-based FTTH, there is nothing to say about the speed of the Internet in Nepal. It is at an excellent level. Broadband internet in Nepal was expensive initially, but the story has been completely changed after CG Net introduced crazy pricing for the internet which forced all the competition to drop the price of Internet in Nepal by a huge margin.
Currently, all the internet service providers are using the same technology and providing a minimum speed of 50Mbps to as high as 1Gbps. Fibre optics has increased so much competition that we can easily get 250-500 Mbps connection for around $10 a month.
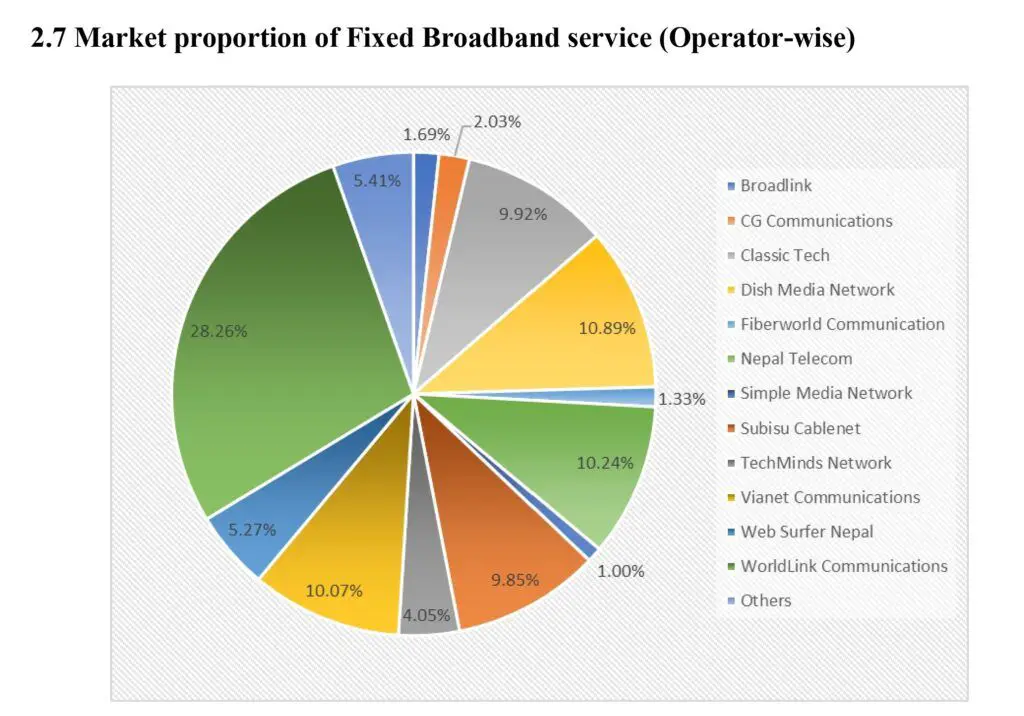
Currently, we can say that broadband internet service based on FTTH is the most affordable service available in Nepal although there is a common misconception about the price of internet in Nepal on the web. But, mobile internet in Nepal is costly compared to India.
The Evolution Of 4G, LTE, VoLTE Internet in Nepal
The fourth generation of the internet was introduced and used in the world in early 2010. It was first launched in India commercially in April 2010 by Airtel.
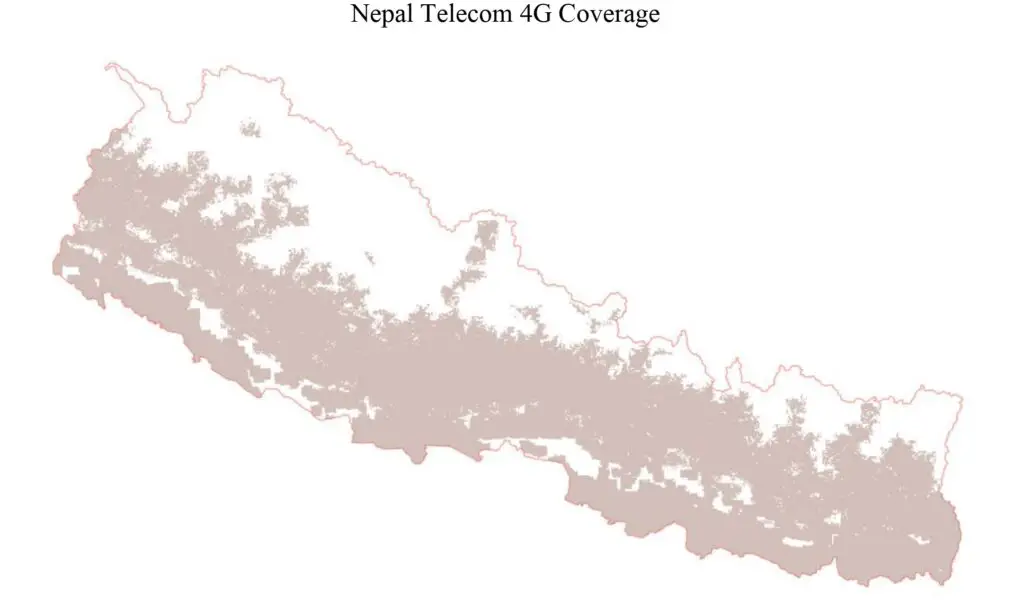
But in Nepal, the Nepal Telecom launched 4G LTE on 1st Jan 2017. That was 7 years after the world and neighboring India. The expansion of this again took a longer time. It took 6 more years to complete complete coverage of 4G internet in Nepal.
While the world was busy using 5G technology, Nepal Telecom was busy expanding its 4G network. Nepal Telecom started VoLTE service as a trial on May 17, 2021, and is now available in all 4G covered areas. This service will enhance audio and video quality and improve connection time. You can also get a 100-minute free voice call in NTC if you enable this service.
5G – The Dirty Politics
5G was introduced in the Mount Everest base camp in the middle of 2020 by the Chinese technology company Huawei. In addition to that, there is no sign of launching 5G in Nepal.
Nepal Telecom had promised that they would introduce 5G before 2022. However, the pandemic made it impossible to complete the work on time. It took some time to get the frequency bandwidth for the connection from the Nepal Telecommunication Authorities.
The board meeting of Nepal Telecommunication Authorities decided to provide 60Mhz frequency bandwidth to NT in its preferred 2600MHz band. Nepal Telecom was all set to start the 5G testing as soon as it got the frequency permit.
Nepal Telecom even started 5G trials in the Sundhara area of Kathmandu on 31 October 2022. But they are forced to close down the 5G connection and there is no publicly accessible 5G connection available in that region.
The main reason is the politics and government. The 5G technology and bandwidth that Nepal Telecom was planning to launch were imported from the Northern side i.e. China. A few months ago it was circulating news that the current government allegedly influenced to stop the launch of 5G based on Chinese technology due to the influence of India and the USA.
This dirty game of politics has caused to delay in the release of 5G even in 2024. Ncell, the only private telecommunication company left in Nepal was not even permitted a 5G frequency band to stop it from using Chinese bandwidth.
Access to the Internet in Nepal in Rural Areas
Although a decent connection was available in the urban areas of Nepal, the accessibility of the internet in Nepalese rural areas was out of the imagination. So, Dr. Mahabir Pun, the Chairperson of the National Innovation Center Nepal made an effort to provide internet in rural areas with his project “Nepal Wireless Networking” in 2002.
This project helped people in geographically backward areas to get access to the internet in Nepal. Mr. Mahabir Pun had installed around 200 wireless internet points in 20 different backward districts. For this contribution, Mr. Pun also received international recognition including the Magsaysay Award for his work in this field.
In addition to this, many private sector ISPs have already expanded in almost all the districts of Nepal with their fiber internet connection. Similarly, Nepal Telecom has already claimed that the 4G coverage has already reached all over Nepal.
Since fiber internet is not affordable in remote regions due to heavy investment and the mobile internet provided by Nepal Telecom and Ncell also has some limitations. However, we can say that access to the internet is pretty good in remote regions of Nepal too.
Growth of Users of the Internet in Nepal
The growth in the number of users of the internet in Nepal is exponential. The penetration rose very quickly after the launch of the 4G connection and it multiplied after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Statistically, there were around 1% population who used the internet in Nepal until 2006. This percentage rose to 9% in 2011 as per a census done during the respective period.
There are two main factors behind this progressive change. The first was the introduction of mobile internet (GPRS) by “Mero Mobile”, now known as NCELL and Nepal Telecom. And the second one is the introduction of ADSL cable internet by Nepal Telecom.
ADSL was the reason, cyber businesses were started in Nepal where the general public who were unable to afford a dedicated personal connection used to go for surfing the internet on a per-hour usage basis.
Current Statistics of Access To The Internet in Nepal
According to a report published by NTA for up to September 2023, the total number of users of fixed broadband connection internet in Nepal has reached 12,722,311. This includes wired and wireless broadband.
The number of mobile broadband users i.e. 3G and 4G SIM users (active users) is 17,431,039 (NTC: 8713063 plus NCELL: 8717976) which also counts corporate users and dual SIM users as individual subscribers.
For more details, you can see the detailed statistics in the following image.

This data shows that the connection access is 139%, which is unrealistic as we have seen many areas not yet covered by a 3G connection. This is because almost every individual with a mobile phone uses dual SIM cards from different providers. Due to the lack of proper records, and regulations in record keeping, the statistics can not represent real data.
Discover more from Grisma Blog
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.